-
-
Sputtering Targets
- Element Sputtering Targets
- Alloy Sputtering Targets
- Oxide Sputtering Targets
- Nitride Sputtering Targets
- Carbide Sputtering Targets
- Fluoride Sputtering Targets
- Silicide Sputtering Targets
- Sulfide Sputtering Targets
- Selenide Sputtering Targets
- Telluride Sputtering Targets
- Antimonide Sputtering Targets
- Phosphide Sputtering Targets
- Special Sputtering Targets Customization
- Sputtering Targets List
-
Evaporation Materials
- Element Evaporation Materials
- Alloy Evaporation Materials
- Oxide Evaporation Materials
- Nitride Evaporation Materials
- Carbide Evaporation Materials
- Fluoride Evaporation Materials
- Phosphide Evaporation Materials
- Telluride Evaporation Materials
- Selenide Evaporation Materials
- Sulfide Evaporation Materials
- Other Evaporation Materials
- Evaporation Materials List
- Compound Semiconductor Materials
- Rare Earth Materials
- Special Alloy
-
Crucible customization
-
Sputtering Targets
- H氢
- He氦
- Li锂
- Be铍
- B硼
- C碳
- N氮
- O氧
- F氟
- Ne氖
- Na钠
- Mg镁
- Al铝
- Si硅
- P磷
- S硫
- Cl氯
- Ar氩
- K钾
- Ca钙
- Sc钪
- Ti钛
- V钒
- Cr铬
- Mn锰
- Fe铁
- Co钴
- Ni镍
- Cu铜
- Zn锌
- Ga镓
- Ge锗
- As砷
- Se硒
- Br溴
- Kr氪
- Rb铷
- Sr锶
- Y钇
- Zr锆
- Nb铌
- Mo钼
- Tc碍
- Ru钌
- Rh铑
- Pd钯
- Ag银
- Cd镉
- In铟
- Sn锡
- Sb锑
- Te碲
- I碘
- Xe氙
- Cs铯
- Ba钡
- LaLu镧系
- Hf铪
- Ta钽
- W钨
- Re铼
- Os锇
- Ir铱
- Pt铂
- Au金
- Hg汞
- Tl铊
- Pb铅
- Bi铋
- Po钋
- At砹
- Rn氡
- La镧
- Ce铈
- Pr镨
- Nd钕
- Pm钷
- Sm钐
- Eu铕
- Gd钆
- Tb铽
- Dy镝
- Ho钬
- Er铒
- Tm铥
- Yb镱
- Lu镥
点击可查看包含对应元素的相关产品信息
科泰新材料可提供“元索周期表”近乎全元素(除放射性元素外)的任意组合材料定制,
部分产品未及时更新,特殊定制需求请咨询客服。
- Al铝
- Ar氩
- As砷
- Ag银
- Au金
- At砹
- Be铍
- B硼
- Br溴
- Ba钡
- Bi铋
- C碳
- Cl氯
- Ca钙
- Cr铬
- Co钴
- Cu铜
- Cd镉
- Cs铯
- Ce铈
- Dy镝
- Eu铕
- Er铒
- F氟
- Fe铁
- Ga镓
- Ge锗
- Gd钆
- H氢
- He氦
- Hf铪
- Hg汞
- Ho钬
- In铟
- I碘
- Ir铱
- K钾
- Kr氪
- Li锂
- LaLu镧系
- La镧
- Lu镥
- Mg镁
- Mn锰
- Mo钼
- N氮
- Ne氖
- Na钠
- Ni镍
- Nb铌
- Nd钕
- O氧
- Os锇
- P磷
- Pd钯
- Pt铂
- Pb铅
- Po钋
- Pr镨
- Pm钷
- Rb铷
- Re铼
- Rn氡
- Ru钌
- Rh铑
- Si硅
- S硫
- Sc钪
- Se硒
- Sr锶
- Sn锡
- Sb锑
- Te碲
- Sm钐
- Ti钛
- Tc碍
- Ta钽
- Tl铊
- Tb铽
- Tm铥
- V钒
- W钨
- Xe氙
- Yb镱
- Y钇
- Zn锌
- Zr锆
当前位置:首页 >> Products >> Sputtering Targets >> Element Sputtering Targets
- 产品类别
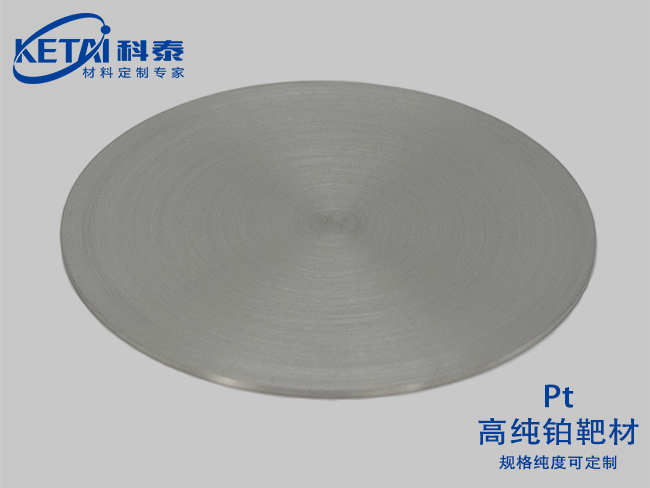
Platinum Sputtering targets(Pt)

| Platinum Sputtering targets(Pt)基本信息 | |
| 分子式 | Pt |
| 纯度 | 99.95% |
| CAS号 | 7440-06-4 |
| 摩尔质量 | 195.078 |
| 密度 | 21.45g/cm3(20℃) |
| 熔点 | 1772℃ |
| 沸点 | 3827℃ |
| 溶解性(水) | |
Platinum Sputtering targets(Pt)产品概况
Platinum is a chemical element, with the chemical symbol Pt. It is one of the precious metals. Its simple substance is commonly known as platinum, and belongs to the platinum series element. Its atomic weight is 195.078, slightly smaller than that of gold. Its atomic number is 78, and it belongs to a transition metal. Melting point 1772 ℃, boiling point 3827 ℃, density 21.45g/cm3 (20 ℃), relatively soft, with good ductility, thermal conductivity, and electrical conductivity. Sponge platinum is a gray spongy substance with a large specific surface area and strong absorption capacity for gases, especially hydrogen, oxygen, and carbon monoxide. Powdered platinum black can absorb large amounts of hydrogen.
Platinum has an inactive chemical property and is stable in air and humid environments. When heated below 450 ℃, a platinum dioxide film forms on the surface, and can react with sulfur, phosphorus, and halogen at high temperatures. Platinum is insoluble in hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, and alkali solutions, but it is soluble in aqua regia and molten alkali. The oxidation states of platinum are+2,+3,+4,+5, and+6. It is easy to form coordination compounds, such as [Pt (NH ⏴) ⏴] Cl ⏴, K [Pt (NH ⏴) Cl ⏴].
| Platinum Sputtering targets(Pt)产品应用 |
Platinum is used as a catalyst in chemical reactions such as hydrogenation, dehydrogenation, isomerization, cyclization, dehydration, dehalogenation, oxidation, and cracking, as well as in the production of sulfuric acid by contact method, nitric acid by ammoxidation, hydrocyanic acid by ammonia and methane, cyclohexane, and vitamins. Reforming naphtha with platinum catalysts can improve the octane number of gasoline products. Platinum and its alloys are resistant to oxidation and corrosion at high temperatures, and are used for making crucibles, evaporating dishes, electrodes, nozzles, reactors, etc. Platinum and platinum rhodium alloys are used as furnace wires and thermocouples for high-temperature furnaces in the metallurgical, glass, and ceramic industries. Platinum is also used to make jewelry.